API Keys & Documentation
Learn how to manage your API keys for programmatic access and integrate with external services using our REST API.
Welcome to your developer hub. This guide provides everything you need to manage your API keys and interact with your content programmatically. Our REST API allows you to build custom integrations, automate workflows, and extend the functionality of your platform.
API Key Management
API keys provide secure, authenticated access to your account's data via the API. You can create multiple keys with different permissions for various applications.
Creating a New API Key
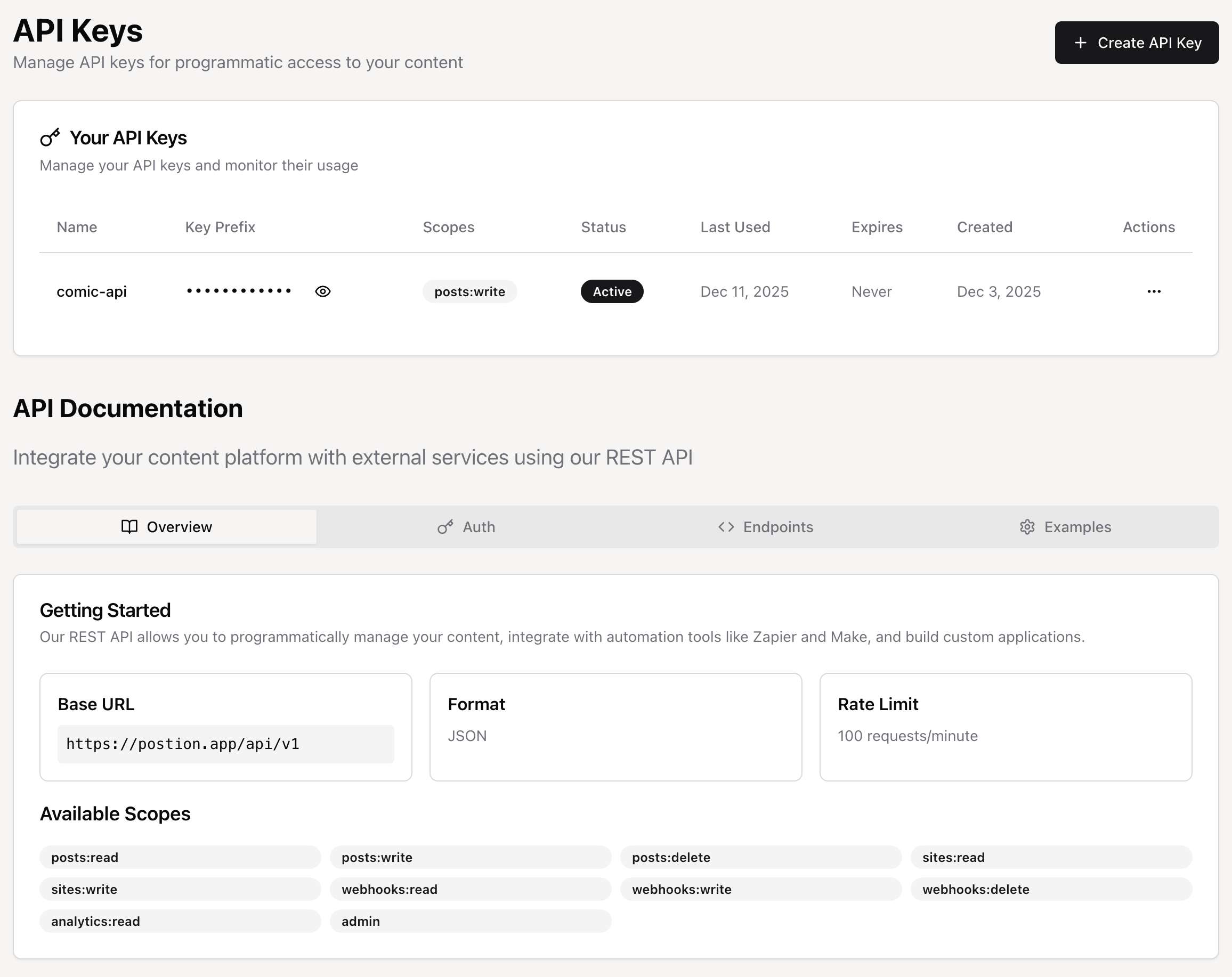
To start using the API, you first need to create an API key.
-
Navigate to the API Keys page in your dashboard.
-
Click the "Create API Key" button.
-
A dialog box will appear where you need to fill in the following information:
- Name: A descriptive name for your key to help you identify it later (e.g., "Zapier Integration", "My Custom App").
- Expiration Date (Optional): For enhanced security, you can set a date and time when the key will automatically expire. Leave it blank for a key that never expires.
- Permissions (Scopes): This is the most crucial part. Select the specific permissions (scopes) that this key will have. Always follow the principle of least privilege: only grant the permissions that your application absolutely needs.
-
Click "Create API Key".
Important: Your new API key will be displayed only once immediately after creation. Make sure to copy it and store it in a secure place. You will not be able to see it again.
Managing Your API Keys
Once created, your API keys will be listed in a table. Here you can manage and monitor them:
- View Key Prefix: For security, only the beginning of your key (
keyPrefix) is stored and displayed. This helps you identify which key is being used without exposing the full secret. - Toggle Visibility: You can click the eye icon (
<Eye />) to temporarily reveal the key prefix. - Status (Active/Inactive): You can activate or deactivate a key at any time. A deactivated key cannot be used to make API requests. This is useful for temporarily disabling an integration without permanently deleting the key.
- Last Used: This column shows the last time the key was successfully used to make an API request, helping you identify unused keys.
- Expires & Created: Shows the expiration and creation dates for the key.
- Actions: The dropdown menu allows you to Activate/Deactivate or permanently Delete a key.
API Documentation
Our API is designed to be predictable and easy to use.
API Overview
- Base URL: All API endpoints are relative to this URL.
https://postion.app/api/v1- Format: All requests and responses are in
JSONformat. - Rate Limit: To ensure stability, the API is rate-limited to 100 requests per minute. Rate limit headers are included in every response.
Authentication
All API requests must be authenticated using a Bearer Token in the Authorization header.
Authorization: Bearer pk_your_api_key_hereReplace pk_your_api_key_here with the secret API key you created.
Example cURL Request
Here is an example of how to fetch a list of your posts using cURL:
curl -X GET "https://postion.app/api/v1/posts" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer pk_your_api_key_here" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json"Security Best Practices:
- Never expose your API keys in client-side code (e.g., in a public website's JavaScript).
- Store your keys securely using environment variables on your server.
- Rotate your API keys periodically.
- Grant only the minimum required scopes for each key.
Endpoints
We provide a range of endpoints to manage your content. Below are some of the main resources available.
Posts
The Posts endpoint allows you to manage your blog posts.
GET /api/v1/posts: List all posts.POST /api/v1/posts: Create a new post.GET /api/v1/posts/{id}: Get a specific post by its ID.PUT /api/v1/posts/{id}: Update a specific post.DELETE /api/v1/posts/{id}: Delete a post.
Sites
The Sites endpoint allows you to manage your sites.
GET /api/v1/sites:List all sites.
Webhooks
Webhooks allow you to receive real-time notifications for events happening in your account.
GET /api/v1/webhooks:List all webhooks.POST /api/v1/webhooks:Create a new webhook.
Code Examples
Here are some practical examples of how to use the API in different programming languages.
JavaScript (Node.js) - Create a Post
const response = await fetch('https://postion.app/api/v1/posts', {
method: 'POST',
headers: {
'Authorization': 'Bearer pk_your_api_key_here',
'Content-Type': 'application/json',
},
body: JSON.stringify({
title: 'My New Post',
content: { /* Your post content in JSON format */ },
description: 'A brief description of my post',
published: true,
tags: ['javascript', 'api']
})
});
const data = await response.json();
console.log('Created post:', data);Python - Fetch Posts
import requests
headers = {
'Authorization': 'Bearer pk_your_api_key_here',
'Content-Type': 'application/json'
}
response = requests.get(
'https://postion.app/api/v1/posts',
headers=headers,
params={'published': True}
)
if response.status_code == 200:
data = response.json()
posts = data['data']
print(f"Found {len(posts)} posts")
else:
print(f"Error: {response.status_code}")Handling Webhooks (Node.js/Express)
It is critical to verify webhook signatures to ensure that the request is legitimate.
// Express.js webhook handler
app.post('/webhook', express.raw({type: 'application/json'}), (req, res) => {
const signature = req.headers['x-webhook-signature'];
const payload = req.body;
// Verify the signature
const expectedSignature = crypto
.createHmac('sha256', process.env.WEBHOOK_SECRET)
.update(payload)
.digest('hex');
if (signature !== expectedSignature) {
return res.status(401).send('Invalid signature');
}
const event = JSON.parse(payload);
// Process the event
switch (event.event.type) {
case 'post.published':
// Handle post publication...
break;
default:
console.log('Unknown event type:', event.event.type);
}
res.status(200).send('OK');
});Additional API Endpoints
Below are more endpoints available for building comprehensive integrations.
Subscribers
Manage your subscriber base programmatically.
| Method | Endpoint | Description |
|---|---|---|
GET | /api/v1/subscribers | List all subscribers |
GET | /api/v1/subscribers/{id} | Get subscriber details |
POST | /api/v1/subscribers | Add a new subscriber |
PUT | /api/v1/subscribers/{id} | Update subscriber info |
DELETE | /api/v1/subscribers/{id} | Remove a subscriber |
Example: Get Subscribers
const response = await fetch('https://postion.app/api/v1/subscribers', {
headers: {
'Authorization': 'Bearer pk_your_api_key_here',
}
});
const { data: subscribers, pagination } = await response.json();
console.log(`Found ${subscribers.length} subscribers`);Plans
Manage subscription plans for your sites.
| Method | Endpoint | Description |
|---|---|---|
GET | /api/v1/plans | List all plans |
GET | /api/v1/plans/{id} | Get plan details |
POST | /api/v1/plans | Create a new plan |
PUT | /api/v1/plans/{id} | Update a plan |
Subscriptions
Access subscription data for your subscribers.
| Method | Endpoint | Description |
|---|---|---|
GET | /api/v1/subscriptions | List active subscriptions |
GET | /api/v1/subscriptions/{id} | Get subscription details |
Transactions
View revenue and transaction history.
| Method | Endpoint | Description |
|---|---|---|
GET | /api/v1/transactions | List all transactions |
GET | /api/v1/transactions/{id} | Get transaction details |
Tags
Manage content tags.
| Method | Endpoint | Description |
|---|---|---|
GET | /api/v1/tags | List all tags |
POST | /api/v1/tags | Create a new tag |
PUT | /api/v1/tags/{id} | Update a tag |
DELETE | /api/v1/tags/{id} | Delete a tag |
Rate Limiting Details
To ensure platform stability, API requests are rate-limited.
Rate Limit Headers
Every API response includes these headers:
| Header | Description |
|---|---|
X-RateLimit-Limit | Maximum requests per window |
X-RateLimit-Remaining | Requests remaining in current window |
X-RateLimit-Reset | Unix timestamp when the window resets |
Rate Limits by Plan
| Plan | Requests per Minute | Requests per Day |
|---|---|---|
| Free | 30 | 1,000 |
| Launch | 60 | 5,000 |
| Pro | 100 | 20,000 |
| Enterprise | Custom | Custom |
Handling Rate Limits
When you exceed the rate limit, you'll receive a 429 Too Many Requests response:
{
"error": {
"code": "RATE_LIMIT_EXCEEDED",
"message": "Too many requests. Please slow down.",
"retry_after": 30
}
}Best Practices:
- Implement exponential backoff when you receive 429s
- Cache responses when possible
- Use webhooks instead of polling for real-time updates
Error Handling
All API errors follow a consistent format.
Error Response Format
{
"error": {
"code": "ERROR_CODE",
"message": "Human-readable error message",
"details": {}
}
}Common Error Codes
| Code | HTTP Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
UNAUTHORIZED | 401 | Invalid or missing API key |
FORBIDDEN | 403 | Key lacks required permissions |
NOT_FOUND | 404 | Resource doesn't exist |
VALIDATION_ERROR | 400 | Invalid request parameters |
RATE_LIMIT_EXCEEDED | 429 | Too many requests |
INTERNAL_ERROR | 500 | Something went wrong on our end |
Pagination
List endpoints support pagination for large datasets.
Query Parameters
| Parameter | Type | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
page | number | Page number | 1 |
limit | number | Items per page | 20 |
sort | string | Sort field | created_at |
order | string | asc or desc | desc |
Pagination Response
{
"data": [...],
"pagination": {
"page": 1,
"limit": 20,
"total": 150,
"total_pages": 8,
"has_next": true,
"has_prev": false
}
}API Changelog
Stay informed about API updates.
Version History
| Version | Date | Changes |
|---|---|---|
| v1.2 | 2025-08 | Added subscribers and transactions endpoints |
| v1.1 | 2025-06 | Added plans and subscriptions endpoints |
| v1.0 | 2025-01 | Initial API release |
Versioning: The API is versioned via the URL path (/api/v1/). Breaking changes will be released as new versions.