Webhooks Documentation
Unlock powerful automations for your content platform. Learn how to use Webhooks to receive real-time HTTP requests for events like new sales or signups.
Overview
Webhooks allow you to receive HTTP requests related to your content platform. When specific events occur (like a new post being created or published), we'll send a POST request to your configured endpoint with details about the event.
Getting Started: Create a webhook in your dashboard, select the events you want to listen for, and provide your endpoint URL. We'll start sending events immediately.
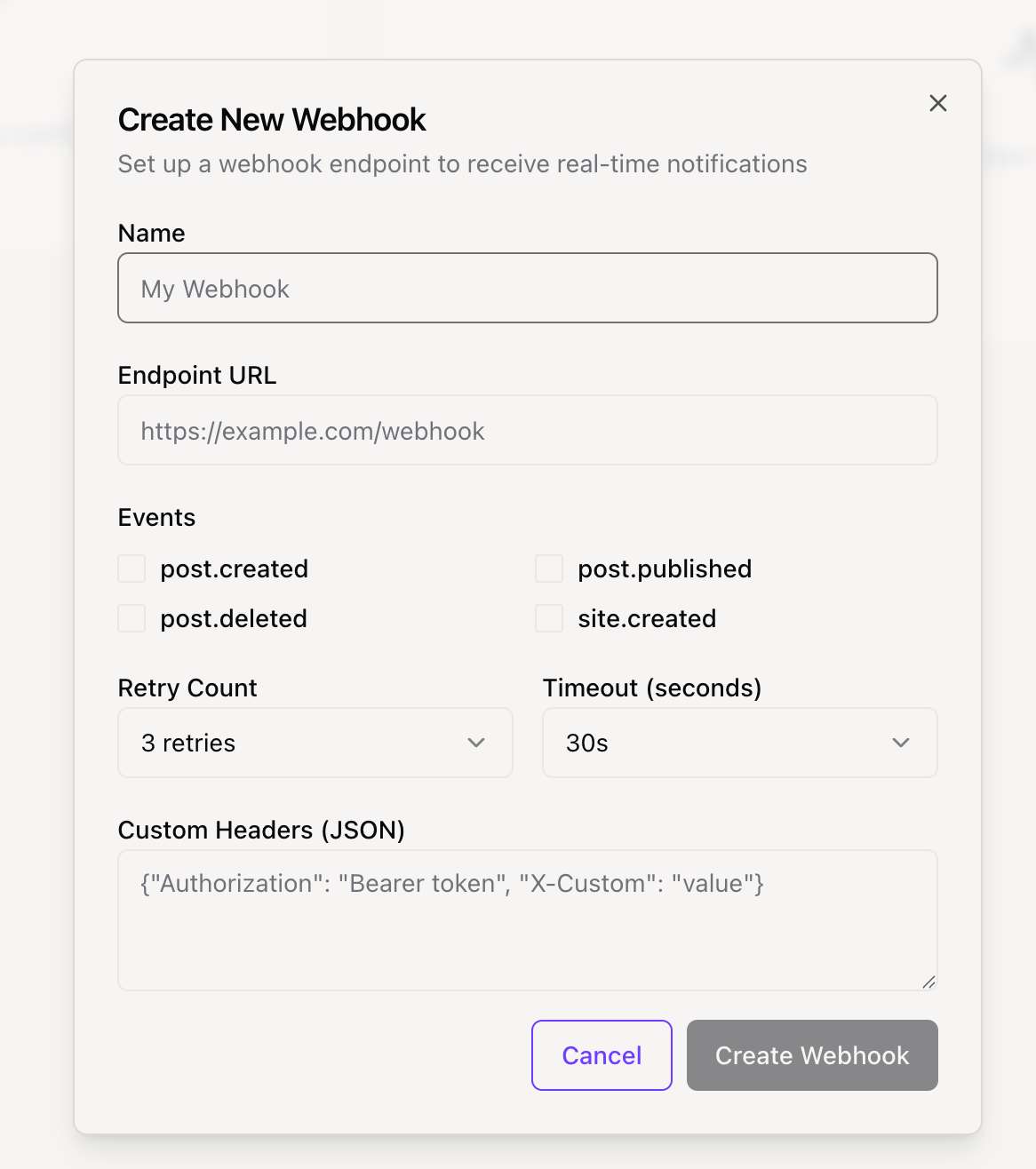
Available Events
There are currently WEBHOOK_EVENTS events you can listen to. Below are the details for each event and an example of its data payload.
export const WEBHOOK_EVENTS = {
// Post events
POST_CREATED: "post.created",
POST_PUBLISHED: "post.published",
POST_DELETED: "post.deleted",
// Site events
SITE_CREATED: "site.created",
// Subscription events
SUBSCRIPTION_CREATED: "subscription.created",
SUBSCRIPTION_CANCELLED: "subscription.cancelled",
TEST: "test.event",
} as constSignature Verification
To ensure security, you should always verify that webhook requests are actually from our platform. We send a signature with each request that you can use for verification.
Signature Header
We send the signature in the X-Webhook-Signature header. The signature is a HMAC-SHA256 hash of the raw request body, created using your webhook's secret key.
X-Webhook-Signature: a1b2c3d4e5f6...Verification Process
- Retrieve your webhook's secret key from your dashboard.
- Compute a HMAC-SHA256 hash from the raw request body using your secret key.
- Compare the hash you computed with the signature from the
X-Webhook-Signatureheader. - Use a timing-safe comparison function to prevent timing attacks.
Implementation Examples
Here are some code examples for handling and verifying webhooks in different programming languages.
const crypto = require('crypto');
const express = require('express');
const app = express();
app.use(express.json());
// Your webhook secret from the dashboard
const WEBHOOK_SECRET = 'your_webhook_secret_here';
function verifySignature(payload, signature) {
const expectedSignature = crypto
.createHmac('sha256', WEBHOOK_SECRET)
.update(payload)
.digest('hex');
return crypto.timingSafeEqual(
Buffer.from(signature, 'hex'),
Buffer.from(expectedSignature, 'hex')
);
}
app.post('/webhook', (req, res) => {
const signature = req.headers['x-webhook-signature'];
const payload = JSON.stringify(req.body);
if (!verifySignature(payload, signature)) {
return res.status(401).send('Invalid signature');
}
const { event } = req.body;
switch (event.type) {
case 'post.created':
console.log('New post created:', event.data.title);
break;
// ... handle other events
default:
console.log('Unhandled event:', event.type);
}
res.status(200).send('OK');
});
app.listen(3000, () => {
console.log('Webhook server running on port 3000');
});Payload Structure
All webhook payloads follow a standard JSON structure.
Standard Payload
The root object contains details about the delivery, the event itself, and the webhook that triggered it.
{
"id": "delivery-uuid",
"event": {
"type": "post.created",
"data": {
"id": "post_123",
"title": "My New Post",
"...": "event-specific data"
},
"timestamp": "2024-01-15T10:30:00Z",
"site_id": "site_789",
"user_id": "user_456"
},
"webhook": {
"id": "webhook_abc",
"name": "My Webhook"
}
}Headers
Each webhook request includes these standard HTTP headers:
- Content-Type: application/json
- X-Webhook-Signature: [signature]
- X-Webhook-Event: [event.type]
- X-Webhook-Delivery: [delivery.id]
- User-Agent: Position-Webhooks/1.0
Best Practices
Follow these best practices to ensure your webhook integration is secure, reliable, and performant.
Security
- Always verify the webhook signature. This is critical to ensure the request is from a trusted source.
- Use HTTPS endpoints to protect data in transit.
- Keep your webhook secret secure and consider rotating it regularly.
Reliability
- Your endpoint must respond with a HTTP 200 status code to acknowledge successful receipt. Any other status code will be considered a failure.
- Design your endpoint to be idempotent. Use the X-Webhook-Delivery ID to detect and handle duplicate events.
- For time-consuming tasks, use a queueing system. Acknowledge the webhook immediately (with a 200 response) and process the task in the background.
Performance
Respond to webhook requests as quickly as possible, ideally within a few seconds. We will time out requests after 30 seconds. Monitor your endpoint's performance and uptime to catch issues before they impact your service.